Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Chettah, A.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
Injecting high-energy heavy ions in the electronic stopping regime into solids can create cylindrical damage zones called latent ion tracks. Although these tracks form in many materials, none have ever been observed in diamond, even when irradiated with high-energy GeV uranium ions. Here we report the first observation of ion track formation in diamond irradiated with 2-9 MeV C fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which
fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which  -bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
-bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
 by using Poisson distribution function
by using Poisson distribution functionYamamoto, Yuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Hori, Fuminobu*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(3), p.26_1 - 26_13, 2020/09
The lattice constant and the magnetic state of CeO are modified by the irradiation with 200 MeV Xe ions. Under the assumption that these modifications are induced in the narrow one-dimensional region (the ion track) along the ion beam path, the dependence of the lattice constant and the saturation magnetization of CeO
are modified by the irradiation with 200 MeV Xe ions. Under the assumption that these modifications are induced in the narrow one-dimensional region (the ion track) along the ion beam path, the dependence of the lattice constant and the saturation magnetization of CeO on the Xe ion fluence can be analyzed by using the Poisson distribution function. The analysis reveals that the lattice constant inside the ion track, which is larger than outside the ion track is not affected by the overlapping of the ion track. The present result implies that the Poisson distribution function is useful for describing the effect of ion track overlapping on the ion irradiation induced ferromagnetic state in CeO
on the Xe ion fluence can be analyzed by using the Poisson distribution function. The analysis reveals that the lattice constant inside the ion track, which is larger than outside the ion track is not affected by the overlapping of the ion track. The present result implies that the Poisson distribution function is useful for describing the effect of ion track overlapping on the ion irradiation induced ferromagnetic state in CeO .
.
 and Nb-doped SrTiO
and Nb-doped SrTiO surfaces irradiated with swift heavy ions
surfaces irradiated with swift heavy ionsKitamura, Akane; Ishikawa, Norito; Kondo, Keietsu; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 460, p.175 - 179, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)Irradiation at grazing incidence formed chains of multiple hillocks on the surface of strontium titanate (SrTiO ) and titanium oxide (TiO
) and titanium oxide (TiO ). They were observed with an atomic force microscope (AFM), however, the AFM measurement gives resolution errors in a nanometer order due to the curvature of the probe tip. To prevent these errors, a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) would be a better option for observation. In this study, we performed SEM observations for the chains of the multiple hillocks. Single crystals of SrTiO
). They were observed with an atomic force microscope (AFM), however, the AFM measurement gives resolution errors in a nanometer order due to the curvature of the probe tip. To prevent these errors, a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) would be a better option for observation. In this study, we performed SEM observations for the chains of the multiple hillocks. Single crystals of SrTiO and TiO
and TiO were irradiated with 200 MeV
were irradiated with 200 MeV  Xe
Xe in the tandem accelerator at JAEA-Tokai. It was revealed that a lot of isolated hillocks were formed in a line on these surface. The diameter and the interval of those hillocks are discussed in comparison to AFM observation.
in the tandem accelerator at JAEA-Tokai. It was revealed that a lot of isolated hillocks were formed in a line on these surface. The diameter and the interval of those hillocks are discussed in comparison to AFM observation.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions
irradiated with swift heavy ionsKitamura, Akane; Ishikawa, Norito; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 44(3), p.85 - 88, 2019/06
Swift heavy ions can create nanosized hillocks on the surfaces of various ceramics. When these materials are irradiated with swift heavy ions at normal incidence, each ion impact results in the formation of a single hillock on the surfaces. In contrast, irradiation at grazing incidence forms chains of multiple hillocks on the surface, for example, for strontium titanate (SrTiO ). So far, chains of multiple hillocks have been investigated using atomic force microscopy (AFM). It should be noted that AFM measurements involve systematic errors of several nanometers due to the finite size of the probe tip. Consequently, it is possible that the image of one hillock may merge with that of a neighboring hillock even if the two hillocks are well separated. In contrast to AFM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) is a useful technique for obtaining higher-resolution images. In this study, we observed multiple nanohillocks on the surfaces of SrTiO
). So far, chains of multiple hillocks have been investigated using atomic force microscopy (AFM). It should be noted that AFM measurements involve systematic errors of several nanometers due to the finite size of the probe tip. Consequently, it is possible that the image of one hillock may merge with that of a neighboring hillock even if the two hillocks are well separated. In contrast to AFM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) is a useful technique for obtaining higher-resolution images. In this study, we observed multiple nanohillocks on the surfaces of SrTiO using FE-SEM. Crystals of SrTiO
using FE-SEM. Crystals of SrTiO (100) and 0.05 wt% Nb-doped SrTiO
(100) and 0.05 wt% Nb-doped SrTiO (100) were irradiated with 350 MeV Xe ions, respectively, at grazing incidence, where the angle between the sample surface and the beam was less than 2
(100) were irradiated with 350 MeV Xe ions, respectively, at grazing incidence, where the angle between the sample surface and the beam was less than 2 . On the SrTiO
. On the SrTiO surface, a chain of periodic nanohillocks is created along the ion path. In contrast, black lines accompanied by hillocks are observed on the Nb-doped SrTiO
surface, a chain of periodic nanohillocks is created along the ion path. In contrast, black lines accompanied by hillocks are observed on the Nb-doped SrTiO surface.
surface.
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Okubo, Nariaki
Nanotechnology, 28(44), p.445708_1 - 445708_11, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:68.85(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)TEM method is applied to Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG) and three fluorides (CaF
(YIG) and three fluorides (CaF , SrF
, SrF and BaF
and BaF ) for observing hillocks. For YIG which is one of the amorphizable materials, hillocks are found to have amorphous feature which is consistent with amorphous feature of ion-tracks. For the fluorides, it is found that the hillocks do not exhibit amorphous feature, and they are composed of nano-crystallites. It is found for the first time that for YIG the hillock diameter is comparable to the ion-track diameter, whereas for the fluorides it is always larger than the ion-track diameter. The results indicate that recrystallization after transient melting plays an important role for formation of hillocks and ion-tracks in fluorides.
) for observing hillocks. For YIG which is one of the amorphizable materials, hillocks are found to have amorphous feature which is consistent with amorphous feature of ion-tracks. For the fluorides, it is found that the hillocks do not exhibit amorphous feature, and they are composed of nano-crystallites. It is found for the first time that for YIG the hillock diameter is comparable to the ion-track diameter, whereas for the fluorides it is always larger than the ion-track diameter. The results indicate that recrystallization after transient melting plays an important role for formation of hillocks and ion-tracks in fluorides.
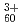 impacts
impactsKitayama, Takumi*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Suzuki, Motofumi*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Isoda, Shoji*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 354, p.183 - 186, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kitabatake, Satomi*; Ushiroda, Tota*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Okahata, Yoshio*; Ito, Atsushi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 86, 2015/03
Biological effects of high-LET radiation could be understood in terms of the ion track structure. Therefore the evaluation of the contribution of both core and penumbra regions to biological effects is an important issue for the study of high-LET effects. In the present study, we developed a protocol to make a uniform DNA sheet with insoluble nature in aqueous solution, and explored the applicability to the detection of 8-OHdG distributions after heavy-ion irradiation. Water-insoluble DNA sheet was irradiated with proton and neon ion beams at JAEA-Takasaki. After irradiation DNA samples were incubated with an 8-OHdG antibody followed by with a second antibody containing a fluorescence probe. The preliminary results indicated that upon ion irradiation randomly distributed dot-like fluorescence was observed, suggesting that these dots may be from incident ions.
Takaki, Seiya*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 326, p.140 - 144, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:94.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated atomic structure of ion tracks in CeO irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). TEM observations under inclined conditions showed continuous ion tracks with diffraction and structure factor contrast, and the decrease in the atomic density of the ion tracks was evaluated. High resolution STEM with high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) technique showed that the crystal structure of the Ce cation column is retained at the core region of ion tracks, although the signal intensity of the Ce cation lattice is reduced over a region nm in size. Annular bright field (ABF) STEM observation has detected that the O anion column is preferentially distorted at the core region of ion tracks within a diameter of 4 nm.
irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). TEM observations under inclined conditions showed continuous ion tracks with diffraction and structure factor contrast, and the decrease in the atomic density of the ion tracks was evaluated. High resolution STEM with high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) technique showed that the crystal structure of the Ce cation column is retained at the core region of ion tracks, although the signal intensity of the Ce cation lattice is reduced over a region nm in size. Annular bright field (ABF) STEM observation has detected that the O anion column is preferentially distorted at the core region of ion tracks within a diameter of 4 nm.
Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Shimada, Mikio*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.235 - 238, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the microstructure change and atomic disordering process in magnesium aluminate spinel, MgO  Al
Al O
O with
with  =1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe
=1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe and 350-MeV Au
and 350-MeV Au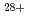 . Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12
. Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12 2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
Koizumi, Hitoshi*; Ichikawa, Tsuneki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.93 - 94, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Reber, N.*; Omichi, Hideki; Spohr, R.*; Tamada, Masao; Wolf, A.*; Yoshida, Masaru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 105(1-4), p.275 - 277, 1995/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:88.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Omichi, Hideki
Radioisotopes, 44(10), p.744 - 758, 1995/10
no abstracts in English
Heinrich, B.*; Lueck, H. B.*; Tamada, Masao; Fischer, B. E.*; Spohr, R.*; Trautmann, C.*; Vetter, J.*; Angert, N.*
GSI-92-1, P. 265, 1992/03
no abstracts in English
; Ono, Shinichi; ; Ito, Hiroshi; Seguchi, Tadao; *
Nucl.Tracks Radiat.Meas., 11(1-2), p.99 - 101, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Kitayama, Takumi*; Morita, Yosuke*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Isoda, Shoji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
no journal, ,
In this study, CeO was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide surfaces, but also at the side faces of the thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the side faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed. From the images of hillocks created at the side faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical. We present an experimental evidence that hillocks created for CeO
was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide surfaces, but also at the side faces of the thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the side faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed. From the images of hillocks created at the side faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical. We present an experimental evidence that hillocks created for CeO irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix. The present method1) of observing hillocks can be a complementary technique to AFM(Atomic Force Microscopy.
irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix. The present method1) of observing hillocks can be a complementary technique to AFM(Atomic Force Microscopy.
 and ZrO
and ZrO
Takaki, Seiya
no journal, ,
Oxide ceramics with fluorite-structure have been studied as advanced nuclear application, so it is important to clarify the irradiation-induced microstructure. Especially, radiation damage induced by fission fragments with 70-100 MeV, induce high-density electronic excitation in the materials to result in forming cylindrical defect, so called ion track. This study aims to clarify and compare with the structure of ion tracks in CeO and cubic ZrO
and cubic ZrO (YSZ) irradiated with swift heavy ions. It was shown that the density of vacancy at the core damage region of ion tracks is increased and the O anion lattice is preferentially disordered at such region. On the other hand, the size and the areal density of ion tracks in YSZ is smaller than those of CeO
(YSZ) irradiated with swift heavy ions. It was shown that the density of vacancy at the core damage region of ion tracks is increased and the O anion lattice is preferentially disordered at such region. On the other hand, the size and the areal density of ion tracks in YSZ is smaller than those of CeO . The difference of ion tracks between CeO
. The difference of ion tracks between CeO and YSZ is presumably due to the difference in the recovery process from the thermal spike regime, which is influenced by the presence of structural vacancy in oxide sublattice.
and YSZ is presumably due to the difference in the recovery process from the thermal spike regime, which is influenced by the presence of structural vacancy in oxide sublattice.
Takaki, Seiya; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
no journal, ,
Advanced nuclear application materials are irradiated by fast neutrons, electrons, a particles and fission fragments, so formation of radiation damage and microstructure evolution are induced by pile-up effect of those radiation. Behavior of point defects in materials which has ion and covalent bonding is influenced by electronic excitation. Especially, high-density electronic excitation damage induced by fission fragments, induce to form cylindrical defect, so called ion track in the materials to result in influence for microstructural evolution in fuel materials. This study aims to clarify the structure of ion tracks in CeO and cubic ZrO
and cubic ZrO (YSZ) irradiated with swift heavy ions by using several transmission electron microscopies. It was shown that the density of vacancy at the core damage region of ion tracks is increased and the O anion lattice is preferentially disordered at such region. In addition to, high density dislocation was formed in CeO
(YSZ) irradiated with swift heavy ions by using several transmission electron microscopies. It was shown that the density of vacancy at the core damage region of ion tracks is increased and the O anion lattice is preferentially disordered at such region. In addition to, high density dislocation was formed in CeO with irradiated by high fluence. This result support STEM observation. In case of YSZ, the size and the areal density of ion tracks is smaller than those of CeO
with irradiated by high fluence. This result support STEM observation. In case of YSZ, the size and the areal density of ion tracks is smaller than those of CeO . The difference of ion tracks between CeO
. The difference of ion tracks between CeO and YSZ is presumably due to the difference in the recovery process from the thermal spike regime, which is influenced by the presence of structural vacancy in oxide sublattice.
and YSZ is presumably due to the difference in the recovery process from the thermal spike regime, which is influenced by the presence of structural vacancy in oxide sublattice.
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Okubo, Nariaki
no journal, ,
Numerous studies have been performed so far for nanometer-sized hillocks created at the irradiated surface of various inorganic materials irradiated with swift heavy ions (SHI). Mechanism of ion track formation in inorganic materials has always been one of the central and intriguing subjects in the SHI research community. It is still challenging to untangle the related problems. A lot of efforts have been recently devoted to answering the questions; Why are radiation-resistant ceramics radiation-resistant? In this talk, the vital part of the recent advancement will be discussed, so that the audience can understand the logical pathway of the latest research works.
Kitamura, Akane; Ishikawa, Norito; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Yamamoto, Shunya*
no journal, ,
Swift heavy ions can create nanosized hillocks on the surfaces of various ceramics. When these materials are irradiated with swift heavy ions at normal incidence, each ion impact results in the formation of a single hillock on the surfaces. In contrast, irradiation at grazing incidence forms chains of multiple hillocks on the surface such as strontium titanate (SrTiO ). So far, chains of multiple hillocks have been investigated using atomic force microscopy (AFM). It should be noted that AFM measurements involve systematic errors of several nanometers due to the finite size of the probe tip. Consequently, it is possible that the image of one hillock may merge with that of a neighboring hillock even if the two hillocks are well separated. In contrast to AFM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) is a useful technique for obtaining higher-resolution images. In this study, we observed multiple nanohillocks on the surfaces of SrTiO
). So far, chains of multiple hillocks have been investigated using atomic force microscopy (AFM). It should be noted that AFM measurements involve systematic errors of several nanometers due to the finite size of the probe tip. Consequently, it is possible that the image of one hillock may merge with that of a neighboring hillock even if the two hillocks are well separated. In contrast to AFM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) is a useful technique for obtaining higher-resolution images. In this study, we observed multiple nanohillocks on the surfaces of SrTiO using FE-SEM. Crystals of SrTiO
using FE-SEM. Crystals of SrTiO (100) and 0.5 wt% Nb-doped SrTiO
(100) and 0.5 wt% Nb-doped SrTiO (100) were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions, respectively. The irradiated angle between the sample surface and the beam was less than 2
(100) were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions, respectively. The irradiated angle between the sample surface and the beam was less than 2 . On the SrTiO
. On the SrTiO surface, a chain of periodic nanohillocks is created along the ion path. In contrast, black lines accompanied by hillocks are observed on the Nb-doped SrTiO
surface, a chain of periodic nanohillocks is created along the ion path. In contrast, black lines accompanied by hillocks are observed on the Nb-doped SrTiO surface. As a result, we proposed a new model of formation process for the hillock chains in the framework of Rayleigh instability.
surface. As a result, we proposed a new model of formation process for the hillock chains in the framework of Rayleigh instability.